# PythonOperator
PythonOperator는 파이썬 Callable 객체(여기엔 함수도 포함됩니다)를 실행하는 Operator입니다.
TIP
파이썬에서는 모든 것이 객체입니다. 심지어 함수도 객체입니다.
Callable 객체에 대해서 처음 들어보신다면 이 글 (opens new window)을 읽어보시길 추천드립니다.
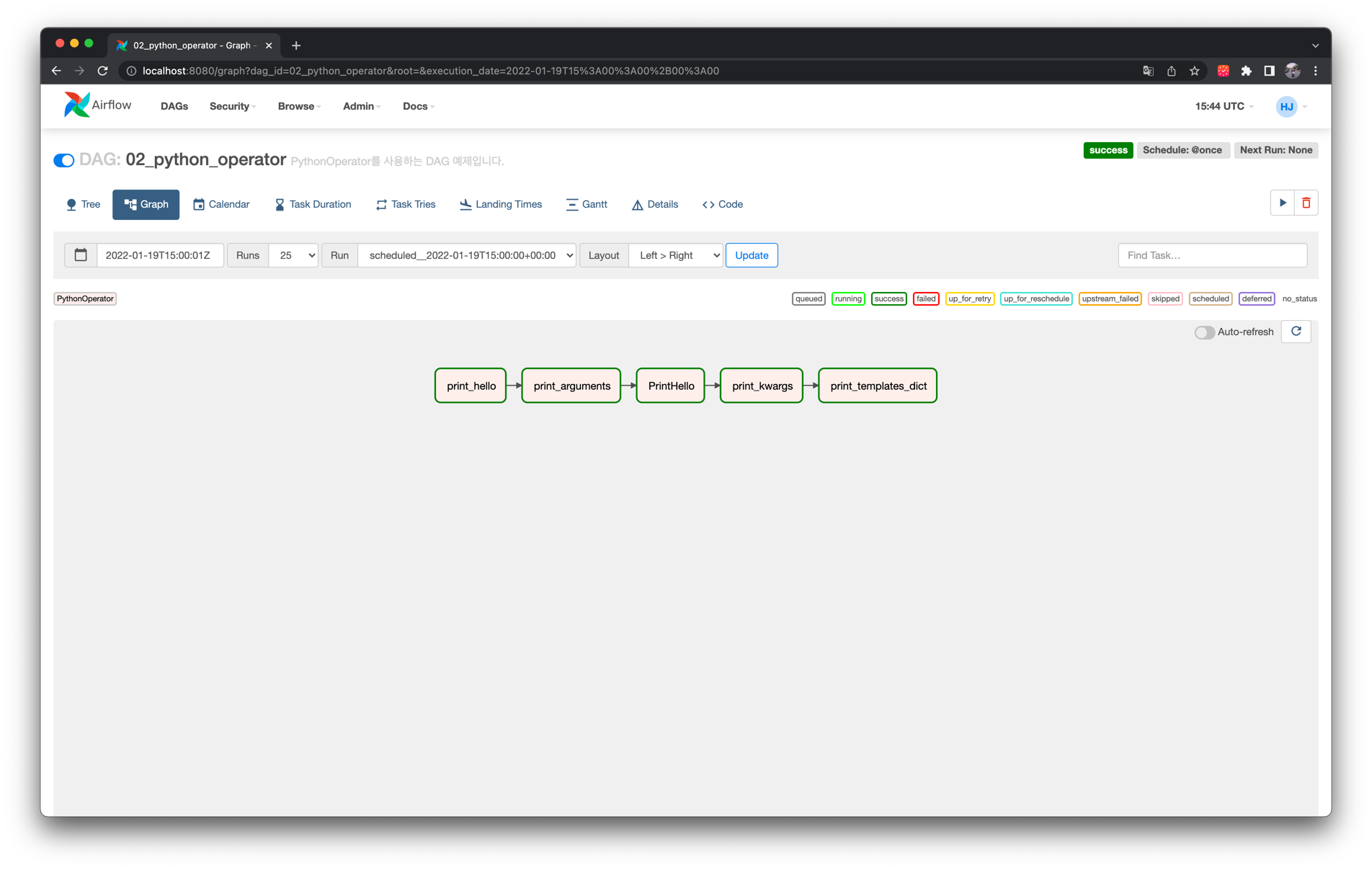
# Graph View
다음처럼 간단한 Task 의존성을 가지는 DAG을 작성해봅시다.
# Code
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
from pendulum.tz.timezone import Timezone
with DAG(
dag_id="02_python_operator",
description="PythonOperator를 사용하는 DAG 예제입니다.",
default_args={
"owner": "heumsi",
"retries": 1,
"retry_delay": timedelta(minutes=1),
},
start_date=datetime(2022, 1, 20, tzinfo=Timezone("Asia/Seoul")),
schedule_interval="@once",
tags=["examples", "04_using_various_operators"],
) as dag:
def print_hello() -> None:
print("hello")
def print_arguments(first_arg: str, second_arg: str) -> None:
print(first_arg)
print(second_arg)
class PrintHello:
def __init__(self, first_arg: str) -> None:
self.first_arg = first_arg
def __call__(self, second_arg: str) -> None:
print(self.first_arg)
print(second_arg)
def print_kwargs(**kwargs) -> None:
print(kwargs)
def print_templates_dict(execution_date: datetime) -> None:
print(execution_date)
task_1 = PythonOperator(task_id="print_hello", python_callable=print_hello)
task_2 = PythonOperator(
task_id="print_arguments",
python_callable=print_arguments,
op_args=["welcome"],
op_kwargs={"second_arg": "airflow"},
)
task_3 = PythonOperator(
task_id="PrintHello",
python_callable=PrintHello(first_arg="welcome"),
op_kwargs={"second_arg": "airflow"},
)
task_4 = PythonOperator(task_id="print_kwargs", python_callable=print_kwargs)
task_5 = PythonOperator(
task_id="print_templates_dict",
python_callable=print_templates_dict,
templates_dict={"execution_date": "{{ ds }}"},
)
task_1 >> task_2 >> task_3 >> task_4 >> task_5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
PythonOperator로 파이썬 Callable 객체를 실행하는 Task Instance를 생성합니다.python_callable파라미터로 실행할 Callable 객체를 넘깁니다.op_args파라미터로 필요한 추가 인자(Arguments)를 넘길 수 있습니다.op_kwargs파마티터로 필요한 키워드 인자(Keyword Arguments)를 넘길 수 있습니다.templates_dict파라미터로 Airflow에서 제공하는 Template 변수를 넘기거나 사용할 수 있습니다.
35-36번째 라인의print_kwargs함수를 보면 작성자가 따로 넘기지 않은kwargs를 출력하고 있습니다.PythonOperator로 실행되는 Callable 객체에는 자동적으로 이런 키워드 인자가 넘어가게 됩니다.- 이에 대한 내용은 아래 결과에서 확인해보겠습니다.
# Web UI
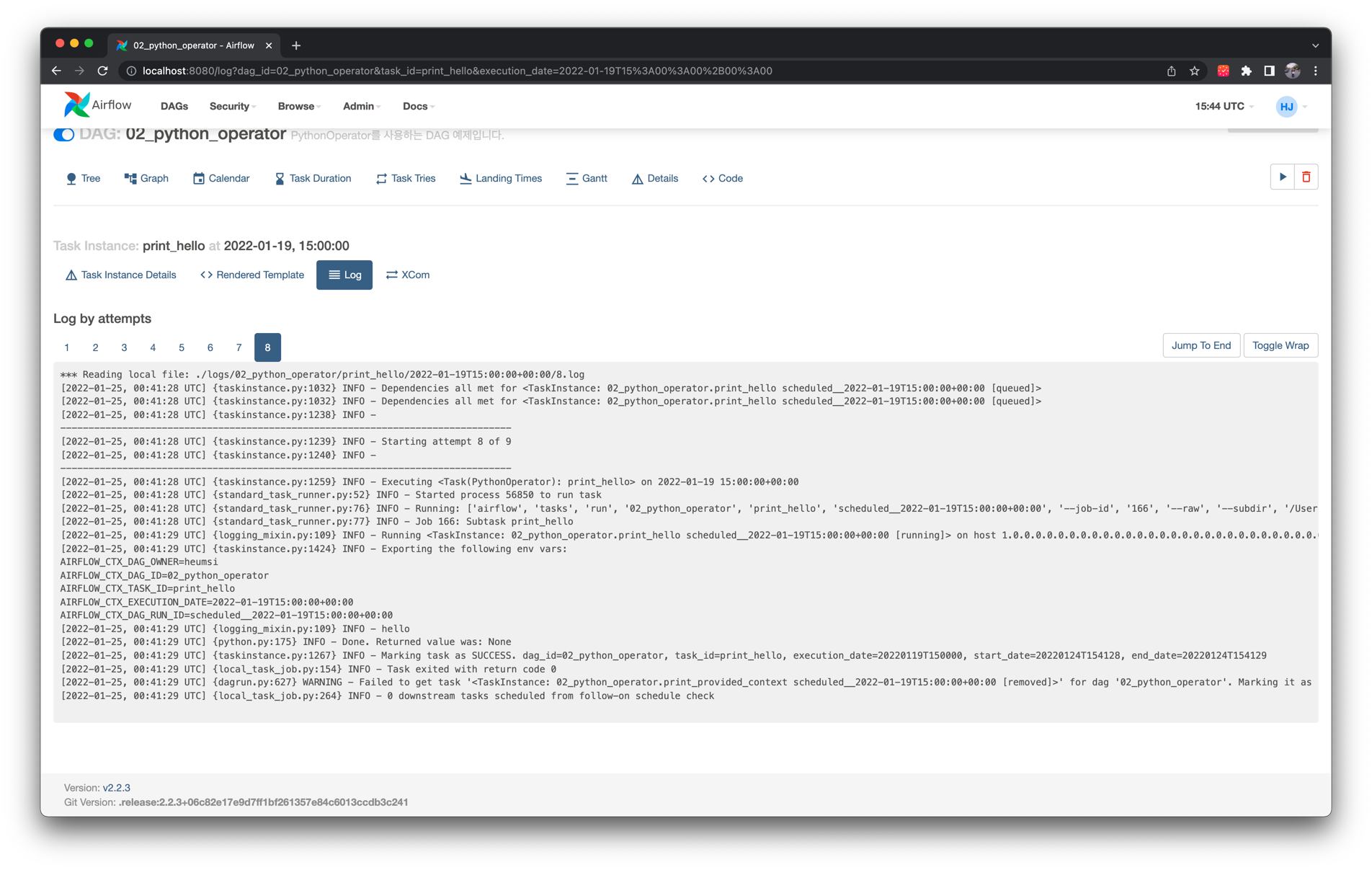
첫 번째 Task Instance인 print_hello 의 로그는 다음과 같습니다.
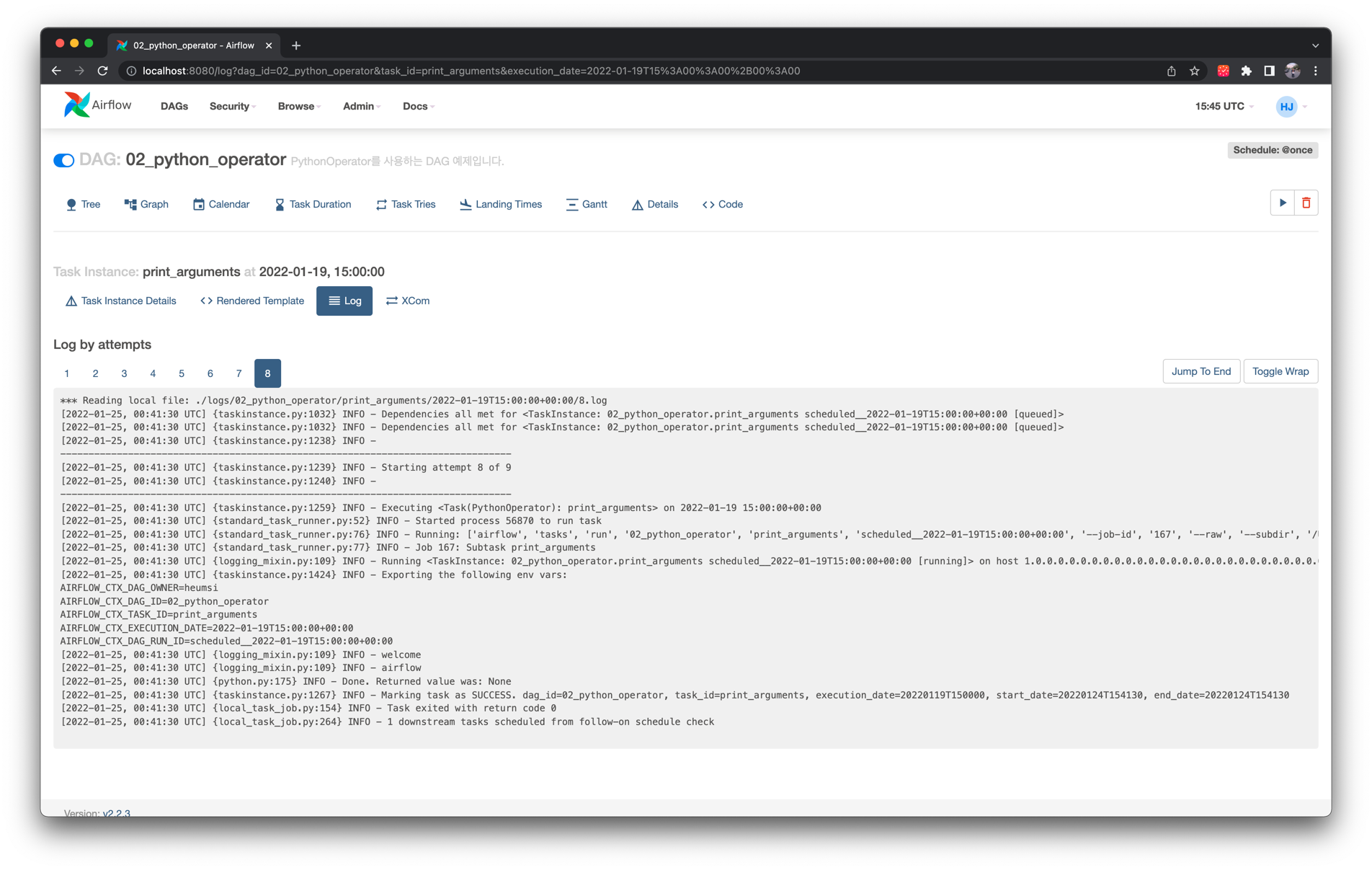
두 번째 Task Instance인 print_arguments 의 로그는 다음과 같습니다.
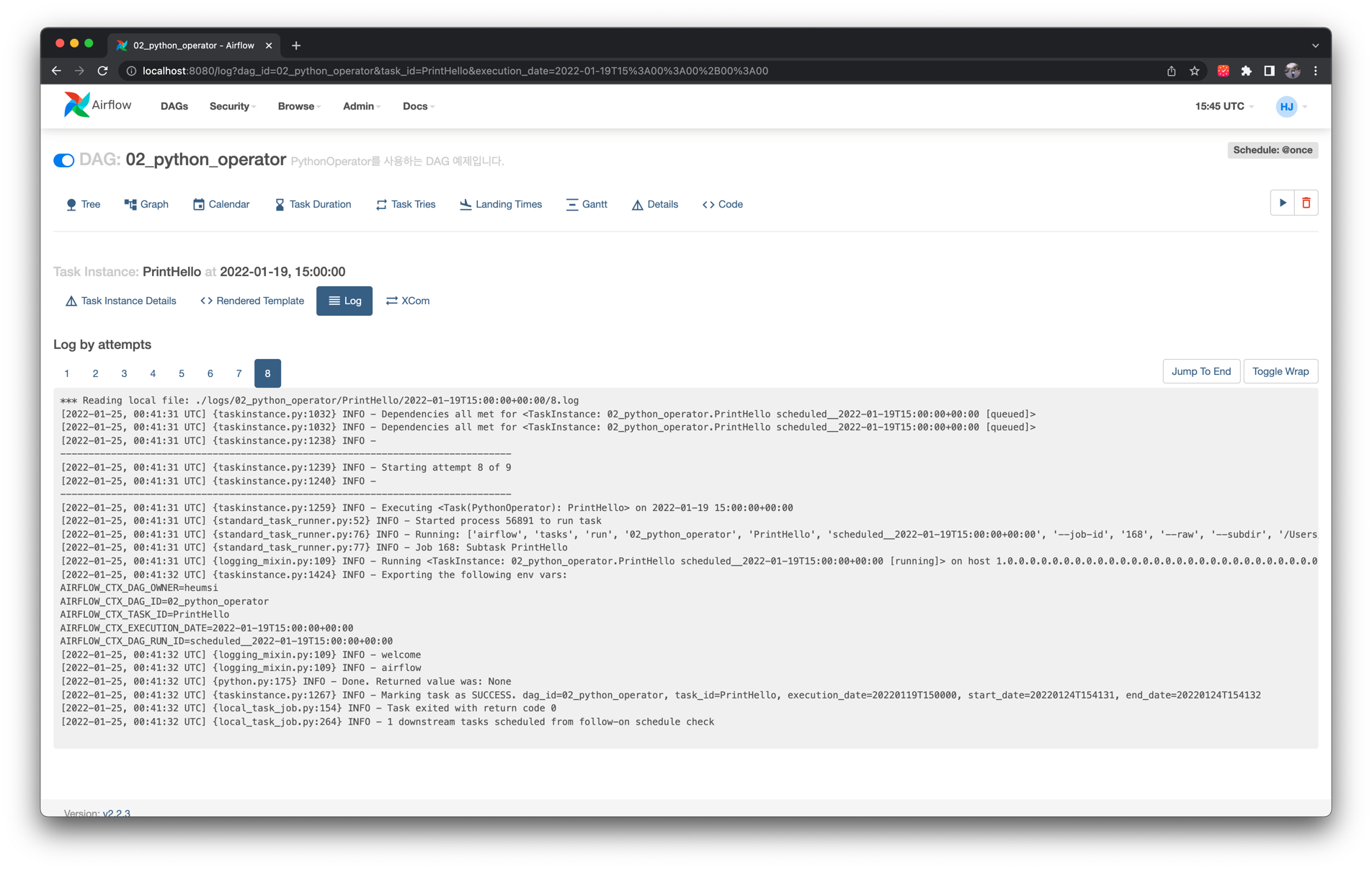
세 번째 Task Instance인 PrintHello 의 로그는 다음과 같습니다.
네 번째 Task Instance인 print_kwargs 의 로그는 다음과 같습니다.
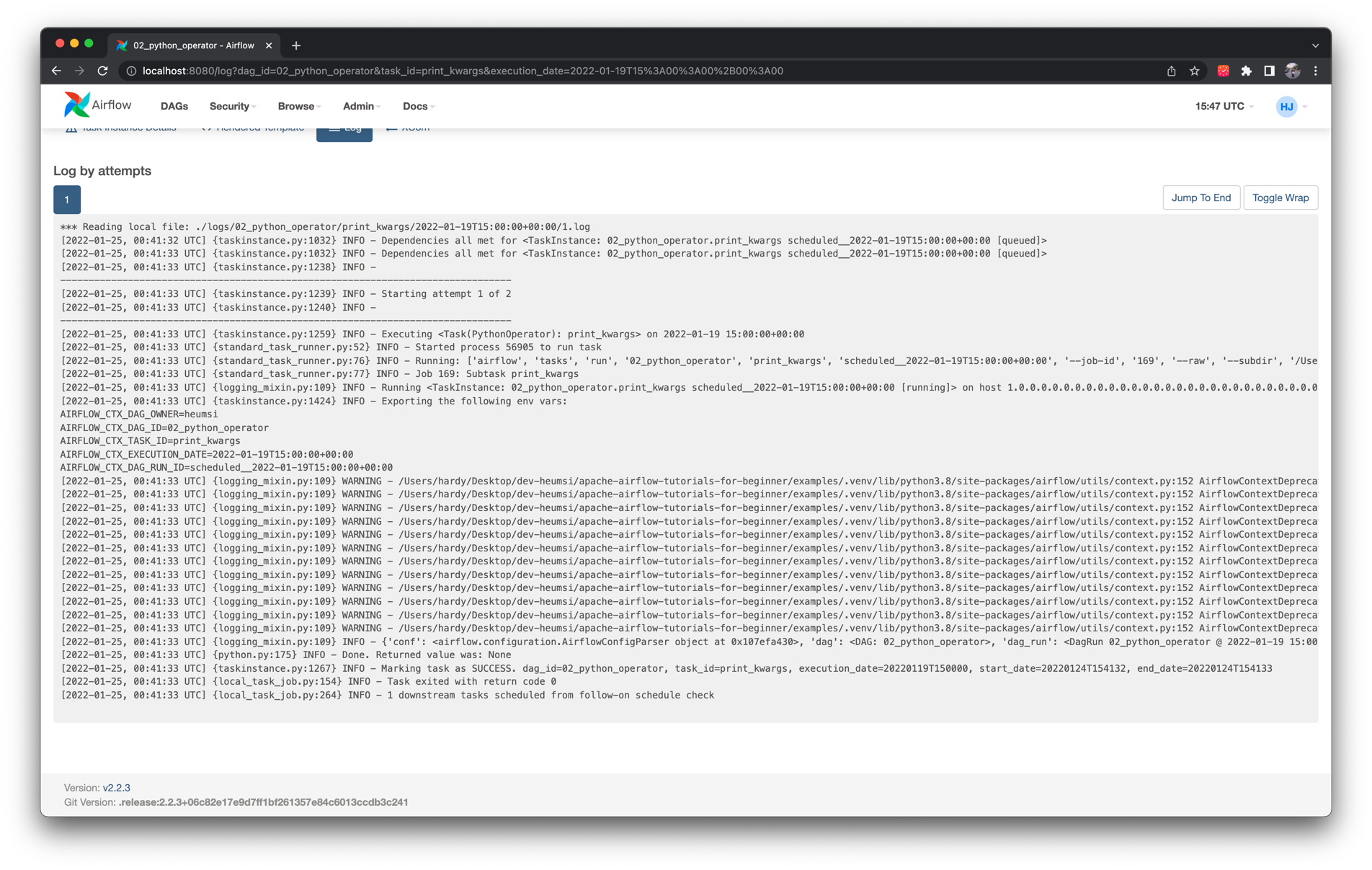
print(kwargs) 로 출력된 결과를 좀 더 자세히 살펴보면 다음과 같습니다.
{
'conf': <airflow.configuration.AirflowConfigParser object at 0x107efa430>,
'dag': <DAG: 02_python_operator>,
'dag_run': <DagRun 02_python_operator @ 2022-01-19 15:00:00+00:00: scheduled__2022-01-19T15:00:00+00:00,
externally triggered: False>,
'data_interval_end': DateTime(2022, 1, 19, 15, 0, 0, tzinfo=Timezone('UTC')),
'data_interval_start': DateTime(2022, 1, 19, 15, 0, 0, tzinfo=Timezone('UTC')),
'ds': '2022-01-19',
'ds_nodash': '20220119',
'execution_date': DateTime(2022, 1, 19, 15, 0, 0, tzinfo=Timezone('UTC')),
'inlets': [],
'logical_date': DateTime(2022, 1, 19, 15, 0, 0, tzinfo=Timezone('UTC')),
'macros': <module 'airflow.macros' from '/Users/hardy/Desktop/dev-heumsi/apache-airflow-tutorials-for-beginner/examples/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/airflow/macros/__init__.py'>,
'next_ds': None,
'next_ds_nodash': None,
'next_execution_date': None,
'outlets': [],
'params': {},
'prev_data_interval_start_success': None,
'prev_data_interval_end_success': None,
'prev_ds': None,
'prev_ds_nodash': None,
'prev_execution_date': None,
'prev_execution_date_success': None,
'prev_start_date_success': None,
'run_id': 'scheduled__2022-01-19T15:00:00+00:00',
'task': <Task(PythonOperator): print_kwargs>,
'task_instance': <TaskInstance: 02_python_operator.print_kwargs scheduled__2022-01-19T15:00:00+00:00 [running]>,
'task_instance_key_str': '02_python_operator__print_kwargs__20220119',
'test_mode': False,
'ti': <TaskInstance: 02_python_operator.print_kwargs scheduled__2022-01-19T15:00:00+00:00 [running]>,
'tomorrow_ds': '2022-01-20',
'tomorrow_ds_nodash': '20220120',
'ts': '2022-01-19T15:00:00+00:00',
'ts_nodash': '20220119T150000',
'ts_nodash_with_tz': '20220119T150000+0000',
'var': {'json': None, 'value': None},
'conn': None,
'yesterday_ds': '2022-01-18',
'yesterday_ds_nodash': '20220118',
'templates_dict': None
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
이 값들은 모두 Scheduler가 이 Task Instance를 실행할 때 주입시켜준 것으로, Task Instance 실행과 관련된 상황(Context) 정보를 담고있습니다.
TIP
이 정보들은 Airflow에서 DAG 작성 시 템플릿 변수로 제공되고 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 공식 문서 (opens new window)를 확인해주세요.
마지막 Task Instnace인 print_templates_dict 의 로그는 다음과 같습니다.
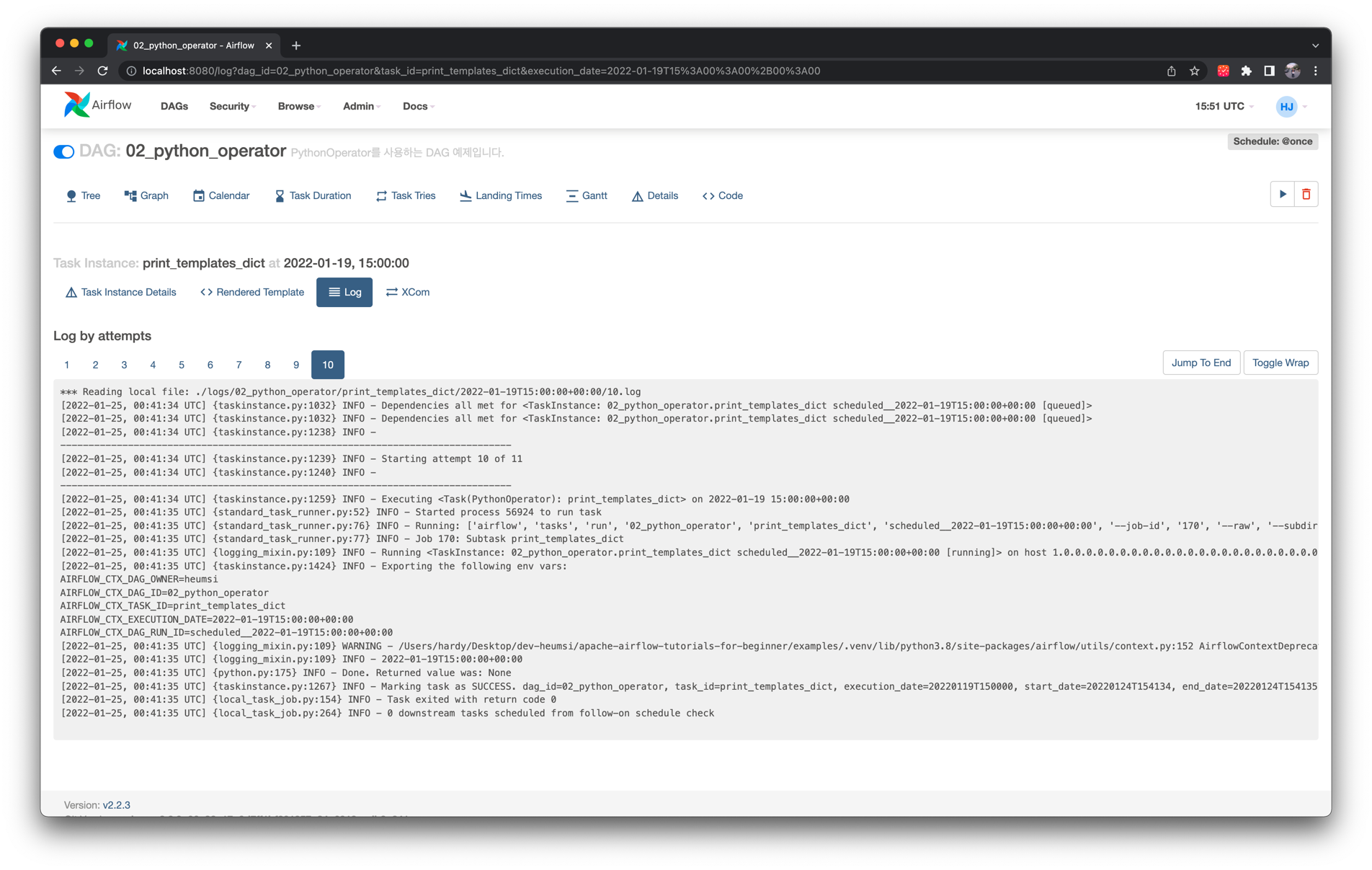
Airflow에서 제공하는 템플릿 변수가 잘 출력된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
